RAID: Redundant Arrays of Independent Disks is a disk group with a huge capacity, which is composed of many cheaper disks. The bonus effect generated by individual disks provides data to improve the efficiency of the whole disk system. Using this technology, the data is cut into many sections and stored on each hard disk, which means an array with redundant ability composed of independent disks.
There are three styles of disk array, one is external disk array cabinet, the other is internal disk array card, and the third is software simulation.
External disk array cabinets are most commonly used in large servers, which have the characteristics of Hot Swap, but the prices of such products are very expensive.
Internal disk array card, because of its low price, needs high installation technology and is suitable for technicians to use and operate. Hardware array can provide online capacity expansion, dynamic modification of array level, automatic data recovery, drive roaming, cache and other functions. It can provide solutions for performance, data protection, reliability, availability and manageability. The special processing unit of the array card is used for operation.

As an independent system, the disk array is directly connected outside the host or connected to the host through the network. A disk array has multiple ports that can be connected by different hosts or different ports. A host connected to different ports of the array can improve the transmission speed.
At that time, like the integrated cache in a single disk for PC, there was a certain amount of buffer memory in the disk array to speed up the interaction with the host. The host interacts with the cache of the disk array, and the cache interacts with specific disks.
(1)RAID 0:consisting of n disks, and the logical capacity is the sum of the capacities of n disks
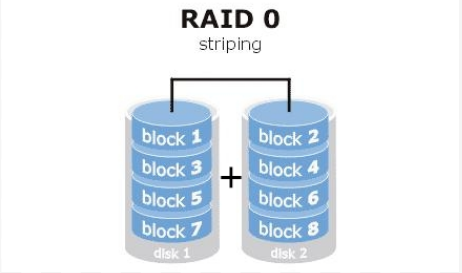
RAID 0 is to combine two or more hard disks into a large-capacity hard disk. It splits the data into different Stripe, and then writes them to all hard disks separately, and reads and writes them at the same time. Because RAID 0 uses multiple hard disks to read and write at the same time, the reading and writing speed of RAID 0 disk array is almost the sum of the speeds of a single hard disk in a unit time, which is much faster than when using a single disk. However, its shortcomings are obvious, it can not improve the random reading efficiency, and the comprehensive data security performance is also low.
(2)RAID 1:The logical capacity is 1 disk
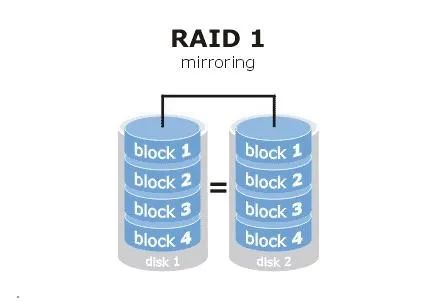
RAID 1 is to copy the data image of one disk to another disk. Take RAID 1 array composed of two hard disks as an example. When data is written into hard disk A, the same image file will be generated on hard disk B.. Simply put, the principle of RAID 1 is a bit like real-time automatic backup. The advantage is high data security, but it also means that the hard disk written into the mirror can only be a "spare tire". After the disk array is completed, the available capacity is only half of the overall capacity.
(3)RAID 5:N disks, and the logical capacity is the sum of N-1 disks
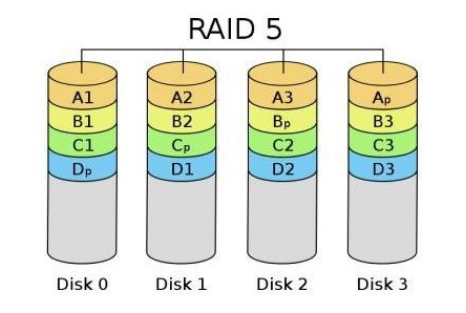
Compared with the two basic disk arrays mentioned above, RAID 5 gives a more balanced consideration to the reading and writing performance and data security. It is composed of three or more hard disks, and in each cycle writing process, the parity of data of other disks is stored in one disk in turn. This means that when any one of the disks is damaged, the system can reconstruct the disk data through the recovery codes stored in other disks, commonly known as disaster tolerance of 1 (data security can be guaranteed on the basis of allowing a hard disk to fail).